Synephrine Causes Greater Fat Usage During Exercise
Table of Contents
Synephrine Causes Greater Fat Usage During Exercise
By: Robbie Durand
p-Synephrine is the primary alkaloid in bitter orange extract that is derived from the immature fruits of Citrus aurantium and many other citrus fruits such as Seville oranges, Nova tangerines, and Marr’s sweet oranges. Synephrine is structurally similar to adrenaline, noradrenaline, and ephedrine. Several studies have confirmed the metabolic effects of synephrine that are useful for bodybuilders such as: enhancing thermogenesis or fat loss.
Synephrine is widely used in combination with caffeine and other ingredients in products designed to support weight management. A previous study reported that 20 mg of synephrine with 325 mg of caffeine increased energy expenditure in humans. In a meta-analysis or collection of studies involving p-synephrine alone or in combination with other nutrients increased resting metabolic rate and energy expenditure by up to ~13 %, and led to modest reductions in body weight. The advantage of p-synephrine is its reduced activation of beta 1 and beta 2 receptors and consequent weak influence in raising blood pressure and heart rate, which mean the substance has fewer side effects than other adrenaline stimulators.
 Synephrine Increases Performance in the Gym
Synephrine Increases Performance in the Gym
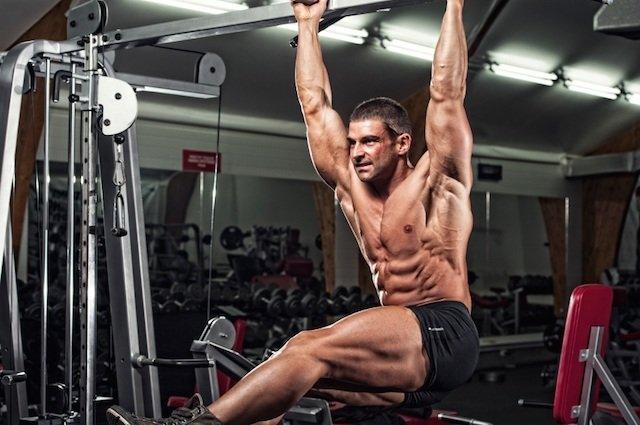
Many supplement companies advocate synephrine and caffeine for weight loss, but according to a new study from the Department of Health and Exercise Science from the College of New Jersey, published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, synephrine can enhance repetitions performed in the gym. There were no studies to date examining the validity of synephrine for performance enhancement, so researchers wanted to put synephrine to the test. The author concluded at the end of the study, “synephrine and synephrine and caffeine augmented resistance exercise performance (total repetitions, volume load).
The addition of synephrine and caffeine increased mean power and velocity of squat performance. These results indicate supplementation with synephrine, and synephrine and caffeine, can enhance local muscle endurance during resistance exercise. The addition of caffeine to p-synephrine resulted in faster, more powerful repetitions.
 Burn More Fat During Exercise with Synephrine
Burn More Fat During Exercise with Synephrine
New research published in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology that p-synephrine’s can enhance more fat burning during exercise. The researcher examined the effects of acute intake of 3 mg p-synephrine per kg body mass on energy metabolism and the rate of fat and carbohydrate oxidation during rest and exercise. In a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, experimental study, 18 subjects underwent two experimental trials: after consuming p-synephrine (3 mg/kg) and after taking a placebo (control test). Energy expenditure and fat oxidation rates were measured by indirect calorimetry at rest and during an exercise cycling test until exercise fatigue was achieved.
An hour after ingesting the substance, energy expenditure and blood pressure, and heart rate were measured before and after physical activity, in this case using a static bike. Acute p-synephrine ingestion had no effect on energy expenditure, heart rate or arterial pressure. This is great news that synephrine is not causing increases in heart rate and blood pressure during exercise. Synephrine ingestion pre-exercise increased the rate of fat oxidation and reduced carbohydrate oxidation at low and moderate intensity. Taking synephrine can contribute to weight loss when combined with exercise and diet.
In sum, the researchers found that:
-Acute consumption of p-synephrine was effective to move the fat oxidation–exercise intensity curve upwards during the incremental exercise and increased maximal fat oxidation rate during exercise.
-The metabolic effects found after the ingestion of p-synephrine might be valuable for those individuals seeking increased fat oxidation during exercise.
Key Points: Synephrine increased fat burning during exercise and may be useful to enhance weight loss.*
Gutiérrez-Hellín J, Coso JD. Acute p-synephrine ingestion increases fat oxidation rate during exercise. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016 Apr 1.
Ratamess NA, Bush JA, Kang J, Kraemer WJ, Stohs SJ, Nocera VG, Leise MD, Diamond KB, Faigenbaum AD. The effects of supplementation with P-Synephrine alone and in combination with caffeine on resistance exercise performance. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015 Sep 17;12:35.
Gougeon R, Harrigan K, Tremblay JF, Hedrei P, Lamarche M, Morais JA. Increase in the thermic effect of food in women by adrenergic amines extracted from Citrus aurantium. Obes Res 2005; 13: 1187–94.
Colker CM, Kaiman DS, Torina GC, Perlis T, Street C. Effects of Citrus aurantium extract, caffeine and St John’s wort on body fat loss, lipid levels and mood states in normal weight and obese individuals. Curr Ther Res 1999; 60: 145–53.