
Liposomal Encapsulation: The Future of Drug Delivery
Table of Contents
The pharmaceutical industry is constantly evolving, and the latest addition to it is Liposomal Encapsulation. It is a technique that uses liposomes as carriers for drugs or active ingredients. Liposome is a small spherical structure made up of a phospholipid bilayer, which makes it similar to cell membranes. The technique has been hailed as the future of drug delivery, as it offers many benefits over traditional methods. In this blog post, we will explore liposomal encapsulation in detail.
We will discuss how it works, its applications in drug delivery and food processing, and how it improves supplement absorption. Additionally, we will look at some case studies that demonstrate the effectiveness of this technique.
Finally, we will discuss the future of liposomal encapsulation and address some concerns about its efficiency and quality.
Understanding Liposomal Encapsulation
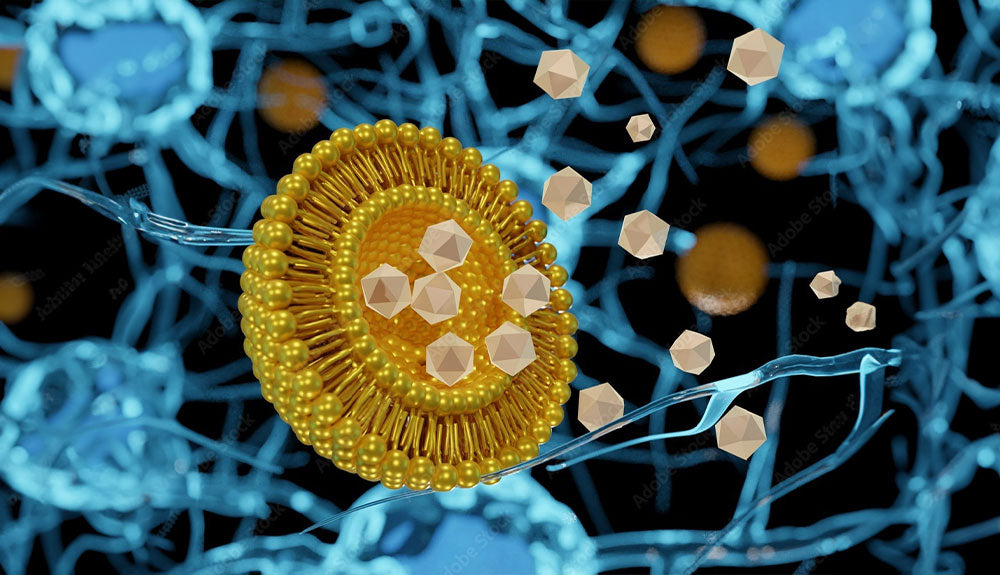
Liposomal encapsulation is a technique used in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and nutrition to deliver substances, such as drugs, vitamins, or nutrients, more effectively to the target cells or tissues in the body. It involves the use of liposomes, which are tiny spherical vesicles composed of lipid (fat) molecules. Liposomes can be used to encapsulate both hydrophobic (fat-soluble) and hydrophilic (water-soluble) substances, making them versatile carriers for various applications.
Here's a breakdown of liposomal encapsulation and how it works:
Liposome Structure:
- Liposomes are typically composed of a lipid bilayer, which consists of two layers of phospholipid molecules. These molecules have hydrophilic (water-attracting) heads and hydrophobic (water-repelling) tails.
- In an aqueous environment, lipids naturally form spherical vesicles with the hydrophobic tails oriented inward and the hydrophilic heads facing outward, creating a water-containing cavity inside the vesicle.
Encapsulation Process:
- To encapsulate a substance within liposomes, the desired substance is mixed with lipids and an aqueous solution. This mixture is then subjected to mechanical or chemical processes such as sonication or extrusion.
- These processes lead to the formation of liposomes with the encapsulated substance trapped within the aqueous core or the lipid bilayer, depending on the properties of the substance and the lipids used.
Applications of Liposomal Encapsulation:
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Liposomes are used to deliver drugs, especially those with low solubility or high toxicity, to improve therapeutic outcomes.
- Nutritional Supplements: Liposomal delivery is employed to enhance the absorption of vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients.

The Process of Liposomal Encapsulation
Liposomal encapsulation involves the preparation of liposomes and the encapsulation of drugs. The process begins with the selection of appropriate phospholipids that form the basic structure of liposomes. Various methods can then be employed to prepare liposomes, such as sonication and extrusion, which help in obtaining liposomes of desired size and stability.
Once the liposomes are prepared, the drug of interest is incorporated into the liposomal structure. This process is known as encapsulation, and it aims to achieve high encapsulation efficiency, which refers to the percentage of drug successfully incorporated into liposomes. Several factors come into play during the encapsulation process, including pH, temperature, and lipid concentration. These factors can impact the stability and integrity of liposomes, as well as the release profile of the encapsulated drug.
The process of liposomal encapsulation represents a promising approach in drug delivery, harnessing the unique properties of liposomes to overcome various challenges associated with traditional drug administration methods. By achieving optimal encapsulation efficiency and understanding the impact of different factors, scientists can unlock the full potential of liposomal drug delivery systems. With advancements in liposomal encapsulation techniques, we can expect even more efficient and targeted drug delivery strategies in the future.
Advancements in Liposomal Encapsulation Techniques
Nanoliposomes, characterized by their size range of 10-100 nm, have emerged as a key advancement in liposomal encapsulation. These tiny liposomes offer improved drug delivery capabilities, allowing for enhanced bioavailability and targeted delivery to specific cells or tissues. By functionalizing liposomes with ligands, such as antibodies or peptides, they can be specifically designed to recognize and bind to receptors on target cells, such as cancer cells or macrophages.
Another significant advancement is the co-encapsulation of multiple drugs in liposomes, enabling combination therapy. This approach allows for the simultaneous delivery of different drugs, which can have synergistic effects and improve treatment outcomes. Liposomes can also be modified to enhance stability and prolong circulation time in the body. This is achieved through various techniques, such as lipid coating or the addition of polymers, which prevent premature degradation and clearance by the immune system.

How Does a Liposome Improve Supplement Absorption?
Liposomes enhance supplement absorption by safeguarding nutrients from digestive enzymes and stomach acid. They also increase bioavailability, allowing more active ingredients to be absorbed. Liposome size and composition impact delivery effectiveness. While liposomal encapsulation shows promise, further research is needed to determine its efficacy.
Liposomal Delivery vs Regular Supplements: A Comparison
Liposomal delivery and regular supplements represent two different approaches to delivering nutrients and medications to the body. Here's a comparison of the two:
Absorption and Bioavailability:
- Liposomal Delivery: Liposomal supplements use lipid (fat) molecules to encapsulate the active ingredient. This protects the nutrient from degradation in the digestive system and allows for better absorption in the gut. Liposomal delivery can significantly enhance bioavailability, meaning more of the nutrient reaches the bloodstream.
- Regular Supplements: Traditional supplements, such as pills and capsules, may have lower bioavailability because they have to go through the digestive system, where they may be broken down or poorly absorbed.
Speed of Absorption:
- Liposomal Delivery: Liposomal supplements are often faster-acting because the liposomes can directly fuse with cell membranes, allowing for quicker absorption into the bloodstream.
- Regular Supplements: Regular supplements typically take longer to be absorbed as they need to be broken down in the stomach and intestines before the active ingredient can enter the bloodstream.
Stability and Shelf Life:
- Liposomal Delivery: Liposomal supplements can be more stable and have a longer shelf life because the liposome encapsulation protects the active ingredient from degradation due to light, heat, and oxygen.
- Regular Supplements: The stability and shelf life of regular supplements vary depending on the form (e.g., tablets, capsules, powders). Some may be less stable and degrade over time.
Taste and Convenience:
- Liposomal Delivery: Liposomal supplements are often available as liquids, which can be more palatable for those who dislike swallowing pills. They are also convenient for mixing into beverages.
- Regular Supplements: Traditional supplements come in various forms, including pills, capsules, and powders, catering to different preferences.
Cost:
- Liposomal Delivery: Liposomal supplements tend to be more expensive than regular supplements due to the specialized technology used in their production.
- Regular Supplements: Regular supplements are generally more affordable, making them a cost-effective option for many people.
Are All Liposomal Supplements Created Equal?
Liposomal supplements differ in terms of encapsulation efficiency and quality. High-quality ones employ natural-source phospholipids, while the manufacturing process determines liposome size and stability. Supplements with suitable lipid bilayer composition offer superior absorption. Seek products that have undergone rigorous bioavailability testing.
Let’s Sum Up
In conclusion, liposomal encapsulation is revolutionizing the field of drug delivery. By using liposomes, scientists can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of delivering drugs to targeted areas in the body. The advancements in liposomal preparation techniques, such as nanoliposomes, have opened up new possibilities for encapsulating a wide range of drugs. Furthermore, liposomal encapsulation has applications beyond pharmaceuticals, with potential benefits in food processing and nutraceuticals.

















