
Liposomal Delivery Systems: Next Generation Breakthrough in Nutrient Absorption
Table of Contents
Are you tired of taking supplements without seeing any visible results? Nutrient absorption is a crucial factor that determines the efficacy of supplements and other oral medications. Traditional nutrient absorption methods have several limitations that can hinder the bioavailability of essential nutrients. But with the advent of liposomal delivery systems, this problem has been resolved to a great extent.
Liposomes are small spherical structures made up of phospholipids that encapsulate nutrients and transport them to the target cells efficiently. In this blog, we will dive deep into the science behind liposomal delivery systems.
We will discuss the various types of liposomes, their manufacturing process, and how they work to enhance nutrient absorption. We will also explore their clinical applications in drug delivery and vaccinations and weigh their advantages and disadvantages.
Lastly, we will shed light on the key factors influencing the efficacy of liposomal delivery systems and how they can revolutionize the nutraceutical industry.
Understanding Liposomes
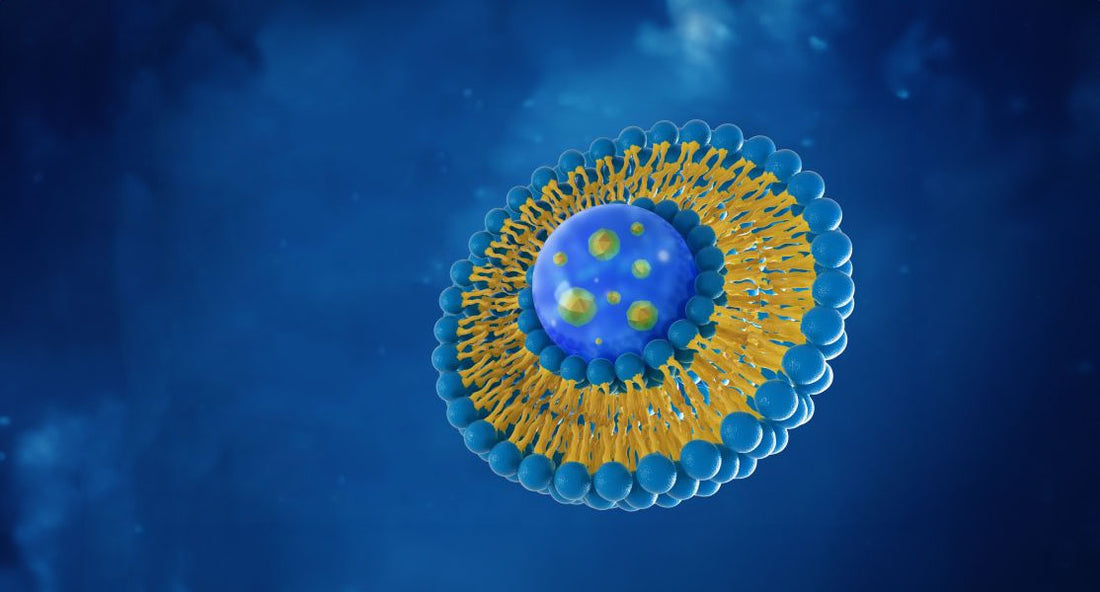
Liposomes, lipid-based structures that mimic cell membranes, play a crucial role in enhancing nutrient absorption. These tiny vesicles can encapsulate various substances, including drugs or nutrients, improving their bioavailability and absorption in the body. Composed of phospholipids, liposomes form a lipid bilayer that allows them to encapsulate substances and protect them during transit. Moreover, liposomes can be modified to target specific cells or tissues, allowing for precise delivery of encapsulated substances.
The unique composition and structure of liposomes make them ideal for nutrient delivery. The phospholipid bilayer of liposomes mimics cell membranes, facilitating easy integration into the body's systems. This integration ensures efficient nutrient delivery and uptake. Additionally, liposomes promote ion transport and improve blood circulation, further enhancing nutrient absorption.
To form liposomes, phospholipids derived from natural sources like soybeans are commonly used. The fatty acid composition of these phospholipids influences the stability and properties of liposomes. Through a controlled manufacturing process, liposomes are produced, ensuring reliable and consistent delivery systems.
Understanding the fundamentals of liposomal delivery systems sets the stage for exploring their significance in nutrient absorption. By utilizing advanced technology and targeted modifications, liposomes hold great promise in delivering nutrients effectively and efficiently to support optimal health.
Composition and Structure of Liposomes
Here's an overview of the composition and structure of liposomes:
Composition: Liposomes are primarily composed of lipids, which are amphiphilic molecules containing hydrophobic (water-repellent) and hydrophilic (water-attracting) regions. The most commonly used lipids for liposome formation are phospholipids, but other lipids like cholesterol may also be included to modify the properties of the liposomes. The choice of lipids greatly influences the stability, size, and release characteristics of the liposomes.
- Phospholipids: These form the basic building blocks of liposomes. Phospholipids consist of a hydrophilic head group (containing a phosphate moiety) and two hydrophobic fatty acid tails. Common phospholipids used in liposome formation include phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, and phosphatidylserine.
- Cholesterol: Cholesterol is often included in liposome formulations to modulate the fluidity and stability of the lipid bilayer. It helps prevent leakage of encapsulated contents and maintains the structural integrity of the liposome.
- Other Lipids: Depending on the desired properties, liposomes can be further modified by including specialized lipids, such as PEGylated lipids (for improved circulation and stealth properties) or cationic lipids (for better interaction with negatively charged molecules or cell membranes).
Structure: The structure of liposomes is characterized by the arrangement of lipid molecules in bilayers. Lipid bilayers consist of two layers of lipid molecules with their hydrophobic tails oriented inward and their hydrophilic heads facing outward toward the aqueous environments. The lipid bilayer structure gives rise to the vesicular nature of liposomes, with an aqueous core enclosed by the lipid membranes.

There are several types of liposomes based on their structure:
- Unilamellar Liposomes: These have a single lipid bilayer enclosing an aqueous core. They can be further classified into small unilamellar vesicles (SUVs) and large unilamellar vesicles (LUVs) based on their size.
- Multilamellar Liposomes: These consist of multiple lipid bilayers stacked concentrically, resembling onion-like structures. Multilamellar liposomes (MLVs) have aqueous compartments between the lipid layers.
- Giant Liposomes: These are much larger liposomes, often ranging in size from tens to hundreds of micrometers. They are used for studying membrane properties and cellular processes.
The size of liposomes can vary widely, from nanometers to micrometers, and can be controlled during the liposome preparation process.
In summary, liposomes are versatile lipid-based vesicles with a defined bilayer structure. Their composition and structure can be tailored to achieve specific properties for various applications, making them valuable tools in drug delivery, research, and other fields.
Various Types of Liposomes Supplements
Liposome supplements have gained popularity due to their potential to enhance the delivery of active ingredients. Here are some common types of liposome supplements:
- Liposomal Vitamin C: Vitamin C is encapsulated within liposomes, which can protect it from degradation in the digestive system and improve its absorption in the bloodstream.
- Liposomal Glutathione: Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant that plays a crucial role in detoxification and immune support. Liposomal delivery can help maintain its stability and increase its uptake by cells.
- Liposomal Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10): CoQ10 is essential for cellular energy production and overall cardiovascular health. Liposomal formulations can enhance its absorption, making it more effective.
- Liposomal Curcumin: Curcumin is a compound found in turmeric with potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Liposomal delivery can improve its bioavailability and tissue uptake.
- Liposomal Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, such as EPA and DHA, are important for brain and heart health. Liposomal encapsulation can protect these sensitive fats from oxidation and improve their absorption.
- Liposomal Resveratrol: Resveratrol is a natural compound found in red wine and certain plants, known for its potential anti-aging and cardiovascular benefits. Liposomal delivery can enhance its stability and absorption.
- Liposomal B Vitamins: B vitamins are essential for various metabolic processes in the body. Liposomal delivery can improve their absorption and utilization.
- Liposomal Magnesium: Magnesium is a mineral important for muscle and nerve function, as well as overall relaxation. Liposomal delivery can enhance its absorption and reduce gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Liposomal CBD: Cannabidiol (CBD) is a compound derived from the cannabis plant, known for its potential relaxation and pain-relief effects. Liposomal delivery can improve its bioavailability.
- Liposomal Iron: Iron is crucial for oxygen transport in the blood and overall energy production. Liposomal delivery can help improve iron absorption and reduce gastrointestinal side effects.
It's important to note that while liposomal supplements may offer enhanced absorption and bioavailability compared to traditional forms, individual responses can vary. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking medications.

The Science of Liposomal Delivery Systems
Liposomal delivery systems have revolutionized drug and nutrient delivery, improving both efficacy and safety. One key advantage of liposomes is their ability to protect encapsulated substances from degradation and metabolism. This ensures that drugs or nutrients reach their intended targets in a more effective manner. Additionally, liposomes can enhance targeted delivery, reducing the risk of side effects by specifically delivering substances to the desired site while minimizing exposure to healthy tissues.
Furthermore, the liposomal membrane can be designed to control release kinetics, allowing for sustained and controlled release of the encapsulated substance. This is particularly useful in cases where a gradual and prolonged release is required for optimal therapeutic or nutritional effects. The science behind liposomal delivery systems has been extensively studied in the field of pharmacology and drug development, leading to a better understanding of their mechanisms and potential applications. Researchers have explored various aspects of liposome formation, including the influence of different lipid compositions, and have investigated ways to optimize liposomal formulations for specific applications.
Clinical Applications of Liposomal Delivery Systems
Liposomal delivery finds applications in various fields, including dietary and nutritional supplements, vaccinations, and drug delivery. Liposomes, with their unique structure, are widely used for encapsulating and delivering nutrients, medications, and even genetic material. The liposomal formulations enable targeted drug delivery and enhance the therapeutic efficacy of anticancer drugs like doxorubicin.
Additionally, liposomes play a crucial role in improving the bioavailability and absorption of nutrients and medications by protecting them from degradation in the digestive system. Their lipid bilayer mimics cell membranes, allowing liposomes to fuse with target cells and release their cargo.
This targeted approach ensures efficient delivery and reduces potential side effects. Liposomal delivery systems have revolutionized the treatment of various diseases by overcoming traditional barriers and improving outcomes through enhanced bioavailability and reduced wastage of nutrients and drugs.
Recent Advances in Liposome Technology
Recent advances in liposome technology have revolutionized nutrient absorption and bioavailability. Liposomal delivery systems, composed of lipid bilayers similar to cell membranes, have emerged as a breakthrough in nutrient delivery. These tiny nanoparticle structures can encapsulate nutrients, such as vitamin C, within their lipid bilayers, protecting them from degradation and ensuring targeted delivery to cells.
One of the key advancements in liposome technology is the development of more stable and efficient liposomes. Researchers have optimized the composition and structure of liposomes, incorporating ingredients like soybean lecithin, which contains essential fatty acids necessary for liposome formation. This has resulted in liposomal delivery systems that demonstrate enhanced efficacy in delivering nutrients to cells.
The applications of liposomal delivery systems extend beyond nutrition. They have found utility in medicine and cosmetics as well. In medicine, liposomes are being explored for targeted drug delivery, while in cosmetics, they are used to enhance the absorption of active ingredients for better skin health.
As research in liposome technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative uses for liposomal delivery systems. The possibilities are vast, from personalized medicine to improved blood circulation and DNA delivery. By harnessing the power of liposomes, scientists are unlocking new frontiers in nutrient absorption and drug delivery.

Future Prospect of Liposomal Delivery Systems
Liposomal delivery systems have demonstrated significant potential in enhancing nutrient absorption, as evidenced by studies reporting notable improvements in bioavailability. This technology holds immense promise for revolutionizing drug delivery, particularly for drugs with poor absorption rates or low bioavailability. Moreover, there is a growing interest in utilizing liposomal delivery systems for targeted drug delivery to specific tissues or cells. Continued research and development in this field could pave the way for more effective and efficient treatments for various diseases and conditions.
Despite its promising future, there are still challenges that need to be addressed. The high production costs associated with liposomal delivery systems pose a hurdle that needs to be overcome. Additionally, further clinical trials are necessary to validate the effectiveness of this technology in real-world scenarios. Nonetheless, the potential benefits make it worthwhile to continue exploring and refining liposomal delivery systems as they hold the potential to significantly enhance drug delivery and improve patient outcomes.
Let’s Sum Up
In conclusion, liposomal delivery systems have revolutionized nutrient absorption and opened up new possibilities in the field of nutraceuticals. These advanced systems, with their unique composition and structure, enhance bioavailability, overcome barriers in traditional nutrient absorption, and reduce wastage of nutrients. From dietary supplements to vaccinations and drug delivery, liposomes have found applications in various clinical settings.
While there are challenges and concerns associated with liposomal delivery, the benefits outweigh them, making it a promising technology. Factors such as ideal composition, size, charge, and stability play a crucial role in determining the efficacy of liposomal delivery systems. With continuous advancements and future prospects, liposomal delivery systems are set to shape the future of the nutraceutical industry.
















